
Born
November 23rd, 1926
Passed Away
April 24th, 2011
Popularly Known as
Sathyanarayana Raju
Occupation
Spiritual Guru and Educator
Native
Puttaparthi
Country
India
Love All, Serve All
Help Ever, Hurt Never
Shradhanjali By
shradhanjali.com
Biography of Sathya Sai Baba
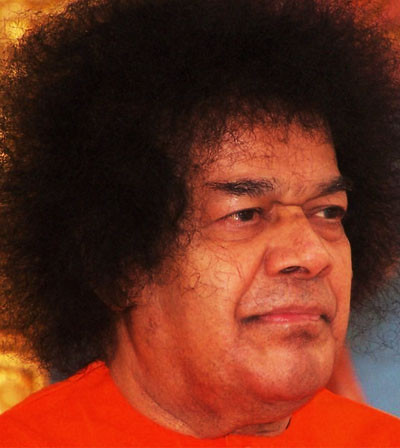

Sathya Sai Baba (Telugu: సత్య సాయిబాబా) born as Sathyanarayana Raju (23 November 1926 - 24 April 2011) was an Indian guru, spiritual figure and educator. In 2011, he was listed by the Watkins Review as one of the 100 most spiritually influential people in the world. He was described by his devotees as an avatar, godman, spiritual teacher and miracle worker. The apparent materialising of vibhuti (holy ash) and other small objects such as rings, necklaces and watches by Baba has been a source of both fame and controversy – skeptics consider these simple conjuring tricks while devotees consider them as signs of divinity. Sathya Sai Baba claimed to be the reincarnation of the spiritual guru, Sai Baba of Shirdi, whose teachings were an eclectic blend of Hindu and Muslim beliefs.
Sathya Sai Baba and his organisations support a variety of free educational institutions, hospitals, and other charitable works in India and abroad. The number of active Sathya Sai Baba adherents was estimated in 1999 to be around 6 million, although followers' estimations are far higher. Since there are no formal ties of membership, the actual figure may never be known. The Sathya Sai Organisation reports that there are an estimated 1,200 Sathya Sai Baba Centers in 114 countries worldwide. In India itself, Sai Baba draws followers from predominantly upper-middle-class, urban sections of society who have the "most wealth, education and exposure to Western ideas." He was a cultural icon in India and drew an audience with presidents and prime ministers from India and beyond who have become his devotees; in 2002, he claimed to have followers in 178 countries.
Life
Almost everything known about his life stems from the hagiography that grew around him, the presentation of narratives that hold special meaning to his devotees and are considered evidence of his divine nature.
Early life and proclamation
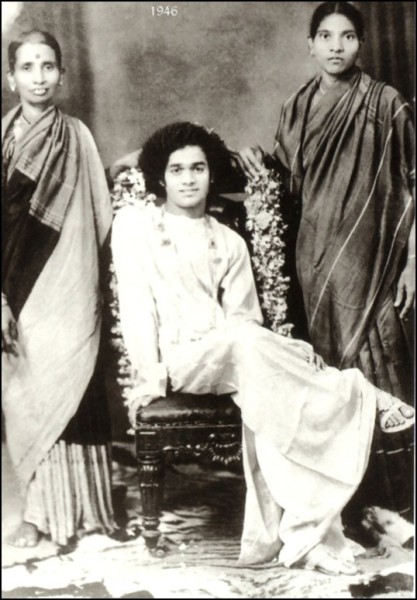
Sathyanarayana Raju was born to Eswaramma and Peddavenkama Raju Ratnakaram in the village of Puttaparthi, in what was the Madras Presidency of British India. His birth, which his mother Eswaramma asserted was by miraculous conception, was also said to be heralded by miracles. As a child, he was described as "unusually intelligent" and charitable. He was exceptionally talented in drama, music, dance and writing, and was an avid composer of poems and plays. He was said to be capable of materialising objects such as food and sweets out of thin air.
On 8 March 1940, while living with his elder brother Seshama Raju in Uravakonda, Sathya was apparently stung by a scorpion. He lost consciousness for several hours. Within the next few days there was a noticeable change in Sathya's behavior. There were "symptoms of laughing and weeping, eloquence and silence."He began to sing Sanskrit verses, a language of which he had no prior knowledge." Doctors believed his behavior to be hysteria. His parents brought Sathya home to Puttaparthi. Concerned, they took him to many priests, "doctors" and exorcists.
On 23 May 1940, Sathya called household members and reputedly materialised prasad and flowers for his family members. His father became furious at seeing this, thinking his son was bewitched. He took a stick and asked him who he was. To this Sathya announced calmly and firmly "I am Sai Baba", a reference to Sai Baba of Shirdi. He proclaimed himself to be a reincarnation of Sai Baba of Shirdi—a saint who became famous in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in Maharashtra and had died eight years before Sathya was born.
Later that year, Sathya Sai Baba declared that he had no worldly relationship with anyone and, around this time, devotees began to gather to him. In 1940, he began to travel to Madras and elsewhere in South India and soon had a large regional following.
Later activities and establishmentsIn 1944, a mandir (temple) for Sathya Sai Baba's devotees was built near the village. It is now referred to as the old mandir. The construction of Prashanthi Nilayam, the current ashram, began in 1948 and was completed in 1950. In 1957 Sathya Sai Baba went on a North Indian temple tour. In 1954, Sathya Sai Baba established a small free General Hospital in the village of Puttaparthi.
In 1963, Sathya Sai Baba suffered a stroke and four severe heart attacks. It is believed by some that he healed himself of these, and on recovering announced that he would be reborn as Prema Sai Baba in the state of Karnataka. He stated, "I am Siva-Sakthi, born in the gothra (lineage) of Bharadwaja, according to a boon won by that sage from Siva and Sakthi. Siva was born in the gothra of that sage as Sai Baba of Shirdi; Siva and Sakthi have incarnated as Myself in his gothra now; Sakthi alone will incarnate as the third Sai (Prema Sai Baba) in the same gothra in Mandya district of Karnataka State." He stated he would be born again eight years after his death at the age of 96.
Sri Sathya Sai University, Puttaparthi, A.P., IndiaOn 29 June 1968, Sathya Sai Baba made his first and only trip overseas, to Uganda. During a discourse in Nairobi, Sathya Sai Baba stated, "I have come to light the lamp of Love in your hearts, to see that it shines day by day with added luster. I have not come on behalf of any exclusive religion. I have not come on a mission of publicity for a sect or creed or cause, nor have I come to collect followers for a doctrine. I have no plan to attract disciples or devotees into my fold or any fold. I have come to tell you of this unitary faith, this spiritual principle, this path of Love, this virtue of Love, this duty of Love, this obligation of Love." In 1968, he established Dharmakshetra or Sathyam Mandir in Mumbai.
In 1973, he established Shivam Mandir in Hyderabad. On 19 January 1981, in Chennai he inaugurated the Sundaram Mandir.
In a 1993 incident, four armed intruders entered his bedroom either as an assassination attempt or as part of a power struggle between his followers. Sai Baba escaped unharmed. During the scuffle and police response the four assailants and two of Sai Baba's attendants were killed. The official investigation left unanswered questions.
In March 1995 he started the water project to provide drinking water to 1.2 million people in the drought-prone Rayalaseema region in Anantapur. In 2001 Sathya Sai Baba established another free Super Speciality hospital in Bangalore to benefit the poor. In April 1999 he inaugurated the Ananda Nilayam Mandir in Madurai, Tamil Nadu.
Illness and death
Sathya Sai Baba said that he would be healthy until age 96 and then die. After 2005 he used a wheelchair and his failing health forced him to make fewer public appearances. In 2006 he suffered a fractured hip when a student standing on an iron stool slipped and both the boy and stool fell on him. After that, he gave darshan from a car or his porte chair.
Sathya Sai Baba was admitted to a hospital at Prashantigram at Puttaparthi on 28 March 2011 following respiration-related problems. After nearly a month of hospitalisation, during which his condition progressively deteriorated, he died on 24 April at 7:40 IST. His funeral is scheduled to be held on 27 April. Many of his devotees, some of whom had held vigil outside the hospital for many days, gathered around the hospital causing law and order concerns. More police were expected to be deployed for his funeral.
His body is expected to lie in state for two days. Karnataka declared 25 and 26 April as days of mourning and Andhra Pradesh declared 25, 26 and 27 April as days of mourning. The government of Karnataka is also organising chartered buses to Puttaparthi. Many of his devotees also paid tribute at a temple.
Political reactions were swift with many offering their condolences, including Prime Minister Manmohan Singh and the Dalai Lama. Others who reacted to his death included Sachin Tendulkar, who canceled his birthday celebrations, although he did play an IPL cricket match in Hyderabad on the day though he refrained from referring to Baba's death.
The Hindu newspaper reported that "Sri Sathya Sai Baba's propagation of spiritualism and preaching of Hindu philosophy never came in the way of his commitment to secular beliefs."
Beliefs and practices of devotees
Sathya Sai Baba said that his followers do not need to give up their original religion, saying "my objective is the establishment of sanatana dharma, which believes in one God as propitiated by the founders of all religions. So none has to give up his religion or deity."
Internationally, Sathya Sai Baba devotees gather daily, or weekly on Sundays or Thursdays or both, to sing group devotional songs, prayer, spiritual meditation, service to the community (Seva), and to participate in "Education in Human Values" (SSEHV) known as "Bal Vikas" (Blossoming of the Child), that can also be described as Sai Sunday School.
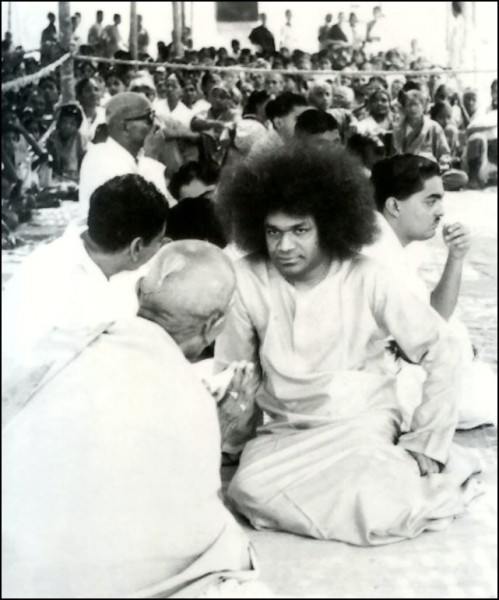
A primary aspect of Baba's teachings is the spiritual benefit of darshan for his students. At that time, Sai Baba might interact with people, accept letters, materialize and distribute vibhuti (sacred ash) or call groups or individuals for interviews. Devotees considered it a great privilege to have an interview and sometimes a single person, group or family was invited for a private interview.
There is no published formal doctrine or set of rules for the Sai Baba movement.
Ashrams and mandirs
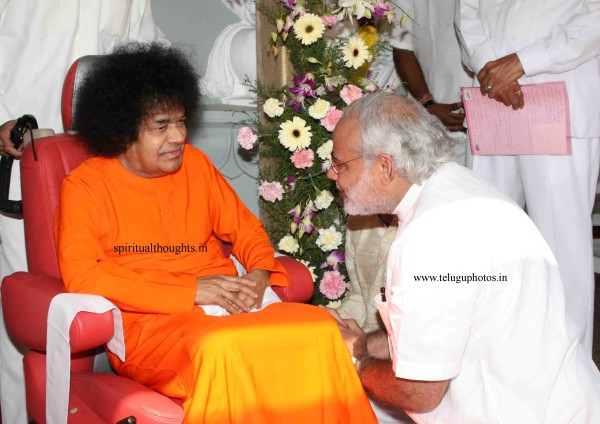
Puttaparthi, where Sathya Sai Baba was born and lived, was originally a small remote South Indian village in Andhra Pradesh. Now there is an extensive university complex, a speciality hospital, Chaitanya Jyoti (a world-religions museum that has won several international awards for design), a Planetarium, a railway station, a hill-view stadium, an administrative building, an airport, an indoor sports stadium and more. High ranking Indian politicians, like the former President Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam, former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Andhra Pradesh former Chief Minister Konijeti Rosaiah and Karnataka Chief Minister B. S. Yeddyurappa have been official guests at the ashram in Puttaparthi. On Sathya Sai Baba's 80th birthday celebration, it was reported that well over a million people attended, including 13,000 delegates from India and 180 other countries.
Sathya Sai Baba resided much of the time in his main ashram called Prashanthi Nilayam (Abode of Highest Peace) at Puttaparthi. In the hot summer he used to leave for his other ashram, called Brindavan, in Kadugodi, Whitefield, a town on the outskirts of Bangalore. Occasionally he visited his Sai Shruti ashram in Kodaikanal.
Sathya Sai Baba established three primary mandirs (spiritual centres) in India. The first mandir, founded in Mumbai in 1968, is referred to as either "Dharmakshetra" or "Sathyam". The second centre, established in Hyderabad in 1973, is referred to as "Shivam". The third centre, inaugurated on 19 January 1981 in Chennai, is referred to as "Sundaram".
Institutions, organisations and projects
Sathya Sai Baba supported a variety of free educational institutions, hospitals, and other charitable works in over 166 countries. The Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Learning (now changed to Sri Sathya Sai University) in Prashanthi Nilayam is the only college in India to have received an "A++" rating by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (an autonomous body established by the University Grants Commission).Sri Sathya Sai University for which Baba is the Chancellor, has three campuses, one at Puttaparthi for men, one at Whitefield, Bangalore for men and one at Anantapur for women. His charity supports an institute for Indian classical music called the Sri Sathya Sai Mirpuri College of Music. Baba's educational institutions aim to impart character education along with excellence in academics with emphasis on human values and ethics.
Sathya Sai Baba chaired the Muddenahalli-Sathya Sai Loka Seva School and Sri Sathya Sai Loka Seva Trust Educational Institutions in Muddenahalli-Kanivenarayanapura regions. In addition, a Sathya Sai Baba University and Medical School as well as a world class hospital and research institute are being constructed on over 200 acres (0.81 km2) to serve the destitute population. Baba said that the campus will be modeled after Puttaparthi and will infuse spirituality with academics.
The Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Medical Sciences in Puttaparthi is a 220 bed facility that provides free surgical and medical care and was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narasimha Rao on 22 November 1991. The Sri Sathya Sai Institute of Higher Medical Sciences in Bangalore is a 333 bed hospital meant to benefit the poor. The hospital was inaugurated on 19 January 2001 by Prime Minister Atal Behari Vajpayee. The hospital has provided free medical care to over 250,000 patients.
The Sri Sathya Sai General Hospital was opened in Whitefield, Bangalore, in 1977 and provides complex surgeries, food and medicines free of cost. The hospital has treated over 2 million patients.
The Sri Sathya Sai Central Trust runs several general hospitals, two specialty hospitals, eye hospitals and mobile dispensaries and conducts medical camps in rural and slum areas in India. The Trust has also funded several major drinking water projects. One project completed in 1996 supplies water to 1.2 million people in about 750 villages in the drought-prone Anantapur district in Andhra Pradesh. The second drinking water project, completed in 2004, supplies water to Chennai through a rebuilt waterway named "Sathya Sai Ganga Canal". Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M. Karunanidhi praised the Chennai water project and Sai Baba's involvement. Other completed water projects include the Medak District Project benefiting 450,000 people in 179 villages and the Mahbubnagar District Project benefitting 350,000 people in 141 villages. In January 2007, the Sri Sathya Sai Central Trust said it would start a drinking water project in Latur, Maharashtra. In 2008, 2 million people in the state of Orissa were affected by floods. As a relief measure, Sri Sathya Sai Seva Organization, has built 699 houses as a part of their first phase in 16 villages by March 2009.
Sathya Sai Baba's Educare program seeks to found schools throughout the world with the goal of educating children in the five human values. According to the Sai Educare site, schools have been founded in 33 countries, including Australia, Mexico, the United Kingdom and Peru. The Times of Zambia states, "The positive influence of Sathya Sai is unprecedented in the annals of education in Zambia. Sai Baba's education ideals as embodied in his human values-based approach in education are an eye opener to educationists in Zambia."
In Canada, the Fraser Institute, an independent Canadian research and educational organization, ranked the Sathya Sai School of Canada as one of the top 37 elementary schools in Ontario. The Sathya Sai School scored a perfect 10 out of 10 in the Institute's overall rating for academic performance.
On 23 November 1999, the Department of Posts, Government of India, released a postage stamp and a postal cover in recognition of the service rendered by Sathya Sai Baba in addressing the problem of providing safe drinking water to the rural masses.
On 23 November 2001, the digital radio network Radio Sai Global Harmony was launched through the World Space Organization, United States. Dr Michael Oleinikof Nobel (distant relative to Alfred Nobel and one of the patrons for the radio network) said that the radio network would spread Sathya Sai Baba's message of global harmony and peace.
In January 2007, an event was held in Chennai Nehru stadium organised by the Chennai Citizens Conclave to thank Sathya Sai Baba for the 200 crore water project which brought water from the River Krishna in Andhra Pradesh to Chennai city. Four chief ministers attended the function.
Reputation for miracles and clairvoyance
Devotees say they have observed Sathya Sai Baba manifesting vibuti (holy ash), and sometimes food and "small objects" such as rings, necklaces and watches. In some books, magazines, filmed interviews and articles, Sathya Sai Baba's followers report miracles of various kinds that they attribute to him. The first ever record of Baba's miracles by a foreigner was made by Howard Murphet in his book, Sai Baba – Man Of Miracles. Devotees have said that objects have appeared spontaneously in connection with pictures and altars of Sathya Sai Baba. Sathya Sai Baba's devotees believe that he relieves his devotees by transferring their pain to himself.
Internationally, devotees report that vibuti, kumkum, turmeric powder, holy water, Shiva lingas, statues of deities (brass and gold), sugar candy, fruits, herbs, amrita (a fragrant, nectar-like honey), gems, colored string, writings in ash and various other substances spontaneously manifest and materialize on the walls, furniture, pictures and altars of Sathya Sai Baba.
The retired Icelandic psychology professor Erlendur Haraldsson wrote that he did not get Sathya Sai Baba's permission to study him under controlled circumstances, but that he investigated the guru's alleged miracles and manifestations through interviews with devotees and ex-devotees. Some of the reported miracles included levitation (both indoors and outdoors), bilocation, physical disappearances, changing granite into sugar candy, changing water into another drink, changing water into gasoline, producing objects on demand, changing the color of his gown while wearing it, multiplying food, healing acute and chronic diseases, appearing in visions and dreams, making different fruits appear on any tree hanging from actual stems, controlling the weather, physically transforming into various deities and physically emitting brilliant light. Haraldsson wrote that the largest allegedly materialized object that he saw was a mangalsutra necklace, 32 inches long, 16 inches long on each side. Haraldsson wrote that some miracles attributed to Sathya Sai Baba resemble the ones described in the New Testament, but that although healings certainly figure in Sai Baba's reputation, his impression is that healings do not play as prominent a role in Sathya Sai Baba's activities as in those of Jesus.
Sathya Sai Baba has explained the phenomenon of manifestation as being an act of divine creation, but refused to have his materializations investigated under experimental conditions. In a 1974 discourse, he stated, "The optical sense cannot visualize the truth. It gives only false and fogged information. For example, there are many who observe my actions and start declaring that my nature is such and such."
In April 1976, H. Narasimhaiah, a physicist, rationalist and then vice chancellor of Bangalore University, founded and chaired a committee "to rationally and scientifically investigate miracles and other verifiable superstitions". Narasimhaiah wrote Sathya Sai Baba three letters that were widely publicized, in which he publicly challenged Baba to perform his miracles under controlled conditions. Sathya Sai Baba said that he ignored Narasimhaiah's challenge because he felt his approach was improper. Sathya Sai Baba further said about the Narasimhaiah committee, "Science must confine its inquiry only to things belonging to the human senses, while spiritualism transcends the senses. If you want to understand the nature of spiritual power you can do so only through the path of spirituality and not science. What science has been able to unravel is merely a fraction of the cosmic phenomena ..." Narasimhaiah's committee was dissolved in August 1977.
According to Erlendur Haraldsson, the formal challenge from the committee came to a dead end because of the negative attitude of the committee, and perhaps because of all the fanfare surrounding it. Narasimhaiah held the fact that Sathya Sai Baba ignored his letters to be one of several indications that his miracles are fraudulent. As a result of this episode, a public debate raged for several months in Indian newspapers.
Indian rationalist Basava Premanand stated, in a BBC documentary, that he had been investigating Sathya Sai Baba since 1968 and that, in his opinion, Sai Baba has faked materialisations. He sued Sai Baba in 1986 for violations of the Gold Control Act, citing Sathya Sai Baba's purported "materializations" of gold objects. When the case was dismissed, Premanand unsuccessfully appealed on the ground that claimed spiritual power is not a defense recognized in law.
A 1995 TV documentary Guru Busters, produced by filmmaker Robert Eagle for UK's Channel 4, Sathya Sai Baba was accused of faking his materializations. The clip from the film was mentioned in the Deccan Chronicle, on 23 November 1992, on a front page headline "DD Tape Unveils Baba Magic". However, Erlendur Haraldsson, a professor of psychology, in his book Modern Miracles stated that, on investigating the DD video, researchers did not find evidence of fake materialisation as claimed by Deccan chronicle. Wiseman took the video to a company which investigates corporate fraud. In spite of improving the graininess of the low quality video with enhanced filters and running it through advanced image processing systems, the DD video did not provide firm evidence of sleight of hand.
In 1998, British journalist Mick Brown stated in his book The Spiritual Tourist that Sathya Sai Baba's claim of "resurrecting" the American devotee Walter Cowan in 1971 was probably untrue. His opinion was based on letters from the attending doctors presented in the magazine Indian Skeptic, published by Basava Premanand, a skeptic and amateur magician. Brown also related, in the same book, his experiences with manifestations of vibuthi from Sathya Sai Baba's pictures in houses in London, which he felt were not fraudulent or the result of trickery. Brown wrote with regards to Sathya Sai Baba's claims of omniscience, that "skeptics have produced documentation clearly showing discrepancies between Baba's reading of historical events and biblical prophecies, and the established accounts."
In December 2000, the magazine India Today published a cover story about Sai Baba with allegations of fakery made by the magician P. C. Sorcar, Jr. Documentaries produced by the BBC and the Danish Broadcasting Corporation, analyzing videos of the supposed miracles, suggested that they can be explained as sleight of hand.
In his book Redemptive Encounters: Three Modern Styles in the Hindu Tradition, Lawrence A. Babb wrote; "Whover he is, he is certainly more than the mere parlour magician many of his critics claim that he is."
Sathya Sai Baba says of "miracles", "those who profess to have understood me, the scholars, the yogis, the pundits, the jnanis, all of them are aware only of the least important, the casual external manifestation of an infinitesimal part of that power, namely, the "miracles"! This has been the case in all ages. People may be very near (physically) to the Avathar (Avatar), but they live out their lives unaware of their fortune; they exaggerate the role of miracles, which are as trivial, when compared to my glory and majesty, as a mosquito is in size and strength to the elephant upon which it squats. Therefore, when you speak about these 'miracles,' I laugh within myself out of pity that you allow yourself so easily to lose the precious awareness of my reality."
Family Tree of Sathya Sai Baba


Eswaramma

Peddavenkama Raju Ratnakaram
Post a tribute & share memories
Fond Memories & Remembrance
Related Profiles
Post Condolences



 Profile Home
Profile Home Biography
Biography Family
Tree
Family
Tree Photo
Album
Photo
Album Video
Video
































































Shradhanjali.com
14 years ago